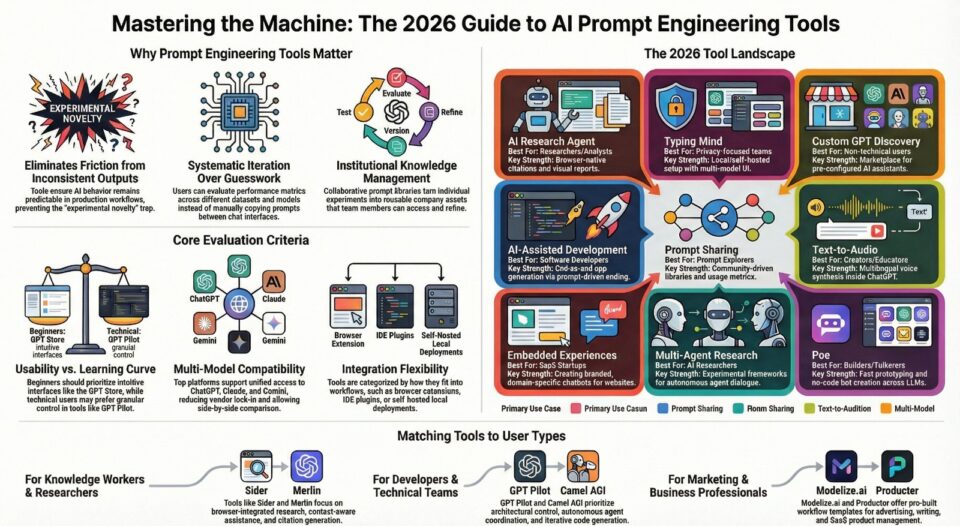
AI prompt engineering tools have become essential infrastructure for anyone working with large language models. These specialized platforms help design, test, version, and optimize prompts to ensure AI outputs meet specific requirements consistently. As organizations scale their use of AI chatbots, research agents, content generators, and autonomous systems, the need for reliable prompt management has grown exponentially.
Prompt reliability matters because inconsistent outputs create friction in production workflows. The best AI prompt engineering tools allow developers and non-technical users alike to iterate rapidly, store reusable templates, evaluate performance across different models, and collaborate on prompt libraries. Both free AI prompt engineering tools and premium platforms offer capabilities that transform AI from an experimental novelty into a dependable component of business operations.
This comprehensive AI prompt engineering tools comparison examines different platforms serving varied use cases, from browser-based research extensions to developer-focused testing frameworks. Understanding which top AI prompt engineering tools align with specific workflows helps teams adopt AI more effectively while avoiding common pitfalls around prompt drift, version control, and quality assurance.
What Are Prompt Engineering Tools?
AI prompt engineering tools are software platforms designed to streamline how users create, test, store, and refine prompts for AI language models. Rather than manually experimenting with prompts in basic chat interfaces, these tools provide structured environments for systematic prompt development. The best AI prompt engineering tools app solutions combine intuitive interfaces with powerful testing capabilities.
Core capabilities typically include prompt versioning, which tracks changes over time and allows rollback to previous iterations. Testing features let users evaluate how prompts perform across different models or datasets. Storage and organization capabilities help teams build reusable prompt libraries categorized by use case, complexity, or domain. Many free AI prompt engineering tools offer basic versions of these features, making experimentation accessible to individual users and small teams.
Real-world applications span multiple domains. Developers use AI prompt engineering tools to build AI-powered features into applications, ensuring consistent behavior in production. Researchers leverage these platforms to design experimental protocols and document methodology. Content creators rely on them to generate blog posts, marketing copy, and creative writing with predictable quality. Business teams adopt prompt libraries to standardize how different departments interact with AI assistants.
These tools bridge the gap between casual AI usage and professional deployment. They introduce discipline and repeatability into workflows that would otherwise depend on individual experimentation and tribal knowledge.
How Prompt Engineering Tools Improve AI Outputs
Predictability represents one of the primary benefits these platforms deliver. When prompts are tested systematically and stored in version-controlled libraries, teams can reproduce results reliably across different sessions and users. This consistency matters especially in customer-facing applications where output quality directly affects user experience.
Quality control mechanisms within prompt engineering software allow users to establish evaluation criteria and benchmark performance. Teams can define success metrics, run batch tests against sample inputs, and identify which prompt variations yield optimal results. This empirical approach replaces guesswork with data-driven decision making.
Iteration speed improves dramatically when tools provide quick feedback loops. Rather than manually copying prompts between applications and tracking results in spreadsheets, users can modify prompts and immediately see comparative outputs. Side-by-side testing across multiple models reveals which platforms handle specific tasks most effectively.
Collaboration features enable team-wide knowledge sharing. Prompt libraries become institutional assets rather than individual experiments. New team members can access proven templates instead of starting from scratch. Subject matter experts can contribute domain-specific prompts that others refine and adapt.
Multi-model support addresses the reality that different language models excel at different tasks. Prompt engineering platforms that integrate with ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and other models let users route tasks to the most appropriate system. A single prompt library can maintain compatibility across providers, reducing vendor lock-in and enabling comparative evaluation.
Evaluation Criteria Used to Compare Tools
This AI prompt engineering tools comparison uses consistent criteria that reflect practical considerations for different user types and workflows.
Usability and learning curve determine how quickly users can become productive. Top AI prompt engineering tools with intuitive interfaces and minimal configuration overhead suit beginners and occasional users. Platforms requiring extensive setup or technical knowledge appeal more to developers willing to invest time for advanced capabilities.
Prompt testing and iteration features include the ability to run prompts against sample data, compare outputs across versions, and evaluate performance metrics. Advanced platforms offer batch processing, automated testing, and quality scoring mechanisms that distinguish professional tools from basic alternatives.
Model compatibility and integration options affect workflow flexibility. The best AI prompt engineering tools support multiple language model providers through unified interfaces, reducing switching costs. Browser extensions, API access, and IDE integrations determine where prompts can be developed and deployed.
Collaboration and storage capabilities separate individual tools from team platforms. Shared prompt libraries, version control, access management, and export functionality enable organizational adoption beyond personal experimentation.
Suitability for different user levels recognizes that beginners need different features than advanced practitioners. Some free AI prompt engineering tools prioritize simplicity and guided experiences, while premium options expose granular control for power users who understand prompt engineering principles deeply.
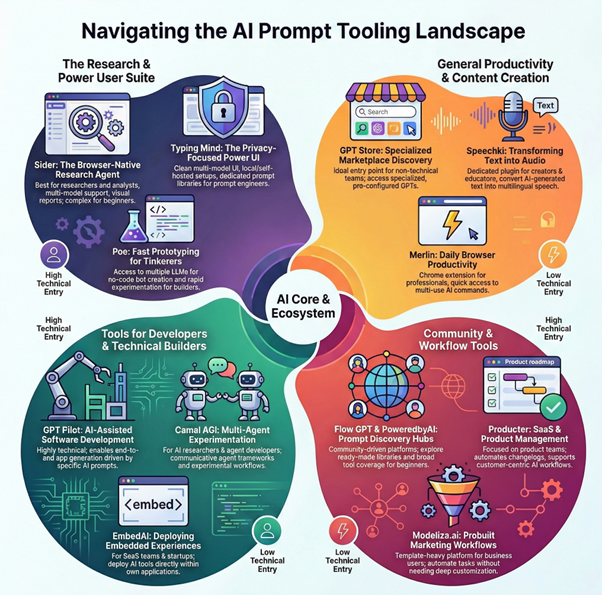
Top Prompt Engineering Tools
Sider: AI Research Agent & Extension
Sider operates as a browser-native research agent designed for users who need to extract, synthesize, and organize information while browsing. The platform integrates directly into web pages through a sidebar interface, allowing researchers and knowledge workers to interact with content without switching contexts.
Key Points:
- Browser sidebar integration for seamless research workflows. Automatic web page scanning with citation generation.
- Multi-model routing across ChatGPT, Claude, DeepSeek, and Gemini. Wisebase personal knowledge storage for saved findings.
- Visual report creation with proper attribution.
- Cross-platform availability on browser extensions, web, and mobile. Artifacts preview for HTML output rendering.
Key capabilities include automatic web page scanning that identifies relevant passages and generates citations. The system creates visual reports with proper attribution, addressing a common challenge in research workflows. Multi-model routing directs different tasks to appropriate language models including ChatGPT, Claude, DeepSeek, and Gemini. A personal knowledge base called Wisebase stores findings for later reference and allows conversational interaction with saved notes.
Strengths center on the integrated research workflow. Rather than managing separate tools for web clipping, note-taking, and AI interaction, users access everything through a unified interface. The citation and attribution features provide accountability often missing from generic AI assistants. Cross-platform availability across browser extensions, web, and mobile ensures access from different devices.
Considerations include feature parity differences across platforms. Capabilities vary between the browser extension, web application, mobile apps, and desktop versions. Extension and mobile history sync exists today, but desktop synchronization remains in development. The artifacts preview for rendering HTML outputs represents an evolving feature set.
Best use cases focus on research-intensive workflows. Academic researchers, journalists, market analysts, and content strategists benefit from the browser integration and citation capabilities. Teams building knowledge bases from web sources find value in the Wisebase storage system. Users who frequently synthesize information from multiple online sources across different browsing sessions represent the core audience.
Typing Mind
Typing Mind positions itself as an enhanced chat interface for daily AI interaction. The platform provides a faster, more customizable alternative to standard model interfaces with emphasis on prompt management and multi-model support.
Key Points:
- Fast multi-model chat interface with seamless switching.
- Built-in prompt library for frequently used prompts.
- Local deployment and self-hosted configuration options.
- Privacy-focused data control. Customizable interface for power users.
- Single-window access to multiple AI providers.
- Productivity-oriented design eliminating tab switching.
Core functionality revolves around a streamlined chat experience that switches seamlessly between different language models. The built-in prompt library allows users to save frequently used prompts and access them quickly. Local deployment options and self-hosted configurations appeal to users concerned about data privacy or working with sensitive information. The interface prioritizes speed and reduces friction compared to navigating between different model providers.
Primary strengths include the snappy user experience and flexible deployment options. Power users appreciate the ability to customize the interface and maintain control over where data resides. The prompt library feature addresses the common need to reuse effective prompts without manual copying. Multi-model support in a single interface eliminates tab switching and credential management across platforms.
Limitations relate primarily to scope. Typing Mind focuses on individual productivity rather than team collaboration. Advanced prompt testing features and evaluation frameworks found in developer-focused tools are not the central value proposition. The platform serves chat-based workflows more than systematic prompt engineering projects.
Ideal users include individuals who interact with AI models throughout their workday for varied tasks. Freelancers, consultants, developers, and knowledge workers who value interface efficiency and prompt reusability represent the target audience. Organizations with strict data residency requirements benefit from self-hosted deployment options.
GPT Store
The GPT Store functions as a discovery platform for custom ChatGPT configurations. Rather than building prompts from scratch, users can browse pre-configured AI assistants designed for specific tasks and industries.
Key Points:
- Marketplace for custom ChatGPT configurations.
- Pre-configured assistants for specific tasks and industries.
- Review and rating system for quality evaluation.
- No-code solution requiring zero prompt engineering.
- Categories spanning productivity, education, creative writing, and programming.
- Immediate access to tested configurations. Community-created specialized GPTs.
The marketplace model connects creators who design specialized GPTs with users seeking ready-made solutions. Categories span productivity tools, educational assistants, creative writing aids, programming helpers, and domain-specific applications. Each custom GPT encapsulates specific instructions, knowledge bases, and behaviors that would otherwise require manual prompt engineering.
Benefits include immediate access to tested configurations built by experienced creators. Users avoid the learning curve of prompt design and can evaluate tools based on reviews and ratings. The variety of available GPTs addresses niche use cases that general-purpose assistants handle less effectively.
Considerations center on dependency and customization limits. Users rely on third-party creators for updates and maintenance. Customization options vary by GPT, with some allowing parameter adjustments while others operate as fixed implementations. Quality varies across offerings, requiring evaluation before adoption.
Best suited for users who prefer curated solutions over building custom prompts. Small business owners, educators, students, and non-technical professionals benefit from domain-specific assistants without engineering overhead. Teams exploring AI applications across different functions can prototype quickly using existing GPTs before investing in custom development.
Speechki ChatGPT Plugin: Anything Audio
Speechki specializes in converting text outputs into audio format directly within ChatGPT workflows. The plugin extends text generation capabilities with multilingual voice synthesis, addressing accessibility and content repurposing needs.
Key Points:
- Text-to-speech conversion within ChatGPT interface.
- Multilingual voice synthesis support.
- Seamless workflow integration eliminating app switching.
- Audio generation from AI text outputs.
- Plugin architecture requiring minimal setup.
- Accessibility-focused features.
- Support for podcast scripts and audiobook creation.
Primary capabilities focus on text-to-speech conversion across multiple languages and voices. Users generate written content through ChatGPT prompts, then convert it to audio without leaving the interface or using separate applications. This integration streamlines podcast script production, audiobook creation, language learning materials, and accessibility adaptations.
Advantages include the seamless workflow integration and multilingual support. Content creators working in audio formats benefit from eliminating manual copy-paste between text generation and speech synthesis tools. The plugin architecture requires minimal setup compared to standalone audio production software.
Constraints relate to the specialized focus. Users seeking comprehensive prompt engineering capabilities beyond audio conversion need complementary tools. Voice quality and customization options depend on the underlying text-to-speech engine and available parameters.
Target audience includes podcasters, audiobook producers, language educators, accessibility specialists, and content creators publishing across text and audio formats. Organizations producing multilingual training materials or customer communications find value in the integrated workflow. Anyone regularly converting AI-generated text into spoken format represents a potential user.
PoweredbyAI
PoweredbyAI operates as a directory and resource hub for AI tools and prompts. The platform aggregates emerging AI applications and provides access to prompt collections across different categories.
Key Points:
- Directory of AI tools and applications.
- Community-contributed prompt library.
- Free access model for exploration.
- Web-based platform requiring no installation.
- Categorized prompt collections by use case.
- Tool discovery for trending AI applications.
- Resource hub for AI enthusiasts and early adopters.
The core offering combines tool discovery with prompt library access. Users explore new AI applications as they launch and find tested prompts organized by use case. The free access model lowers barriers to experimentation. Web application delivery requires no installation, making resources available from any browser.
Value proposition centers on staying current with AI developments and accessing community-contributed prompts. Early adopters and AI enthusiasts use the platform to track new releases and trending applications. The prompt library provides starting points for common tasks without requiring prompt engineering expertise.
Limitations include reliance on community contributions for prompt quality and coverage. Directory-style platforms often favor breadth over depth, meaning individual tools receive less detailed analysis than specialized reviews. Users still need to evaluate and adapt prompts for their specific requirements.
Best suited for users exploring the AI tool landscape and seeking prompt inspiration. Marketers, entrepreneurs, and technology enthusiasts monitoring AI trends benefit from the aggregated view. Teams evaluating multiple tools for specific workflows can use the directory to identify candidates worth deeper investigation.
Flow GPT
Flow GPT functions as a community-driven platform for sharing and discovering ChatGPT prompts. The emphasis falls on workflow amplification through reusable prompt templates contributed by users worldwide.
Key Points:
- Community-driven prompt sharing platform.
- Browse prompts by category, popularity, and use case.
- Free access to extensive prompt collections.
- User ratings and usage metrics for validation.
- Productivity-focused organization scheme.
- Business workflow optimization templates.
- Diverse prompt library from global contributors.
Platform mechanics revolve around prompt submission, curation, and discovery. Contributors share prompts they have developed and tested, while other users browse by category, popularity, or use case. The free access model encourages wide participation. Productivity focus surfaces in the organization scheme, which prioritizes business workflows and professional applications.
Primary advantages include the diversity of contributed prompts and the community validation through ratings and usage metrics. Users benefit from collective experimentation rather than individual trial and error. Specific prompts for niche tasks often surface through community contributions faster than they appear in commercial tools.
Challenges include variable prompt quality and the need for user evaluation. Community platforms depend on contributor motivation and expertise, which fluctuates. Organization and search functionality determine how easily users find relevant prompts among large collections. Prompts require adaptation to specific contexts despite promising descriptions.
Ideal for users comfortable evaluating and adapting prompts rather than seeking fully packaged solutions. Developers, content creators, and business professionals seeking inspiration or starting points benefit from the variety. Teams building internal prompt libraries can source ideas from community examples and refine them for organizational needs.
Producter
Producter serves as a product management platform for customer-centric SaaS startups, with prompt engineering capabilities supporting the broader workflow management focus.
Key Points:
- Product management platform with AI integration.
- Project management and team collaboration tools.
- Customer support tool integration.
- SaaS-oriented productivity features.
- AI assistance within product development cycles.
- Unified platform for managing prompts alongside development artifacts.
- Customer feedback and roadmap management with AI support.
Core functionality spans project management, team collaboration, and customer support tools. The productivity and SaaS orientation distinguishes Producter from pure prompt engineering platforms. Integration capabilities allow teams to incorporate AI assistance into product development cycles without maintaining separate systems.
Strengths emerge in the unified platform approach. Product teams working on AI-powered features can manage prompts alongside other development artifacts. The customer support integration enables teams to leverage AI for user communication while maintaining context with product roadmaps and issue tracking.
Considerations involve the platform scope. Teams seeking specialized prompt testing frameworks may find the capabilities integrated into broader project management less comprehensive than dedicated tools. The value proposition depends on whether organizations benefit from consolidating product management and AI workflow tools.
Target users include product managers, SaaS founders, and development teams building AI-enhanced applications. Organizations that value consolidated tooling over specialized point solutions find appeal in the integrated approach. Startups managing customer feedback, roadmaps, and AI feature development in parallel represent the core market.
Merlin: ChatGPT Powered Chrome Extension
Merlin integrates ChatGPT functionality directly into the browser through a keyboard-activated extension. The tool emphasizes quick access to AI assistance while browsing without switching contexts or applications.
Key Points:
- Keyboard-activated browser extension with Cmd+M hotkey.
- ChatGPT integration within any webpage.
- Context-aware AI assistance based on visible content.
- Chrome extension architecture for seamless browsing.
- Instant AI access without tab switching.
- Browser-native prompt interaction.
- Productivity gains through reduced context switching.
Primary capability centers on the command-M hotkey that summons AI interaction from any webpage. This browser-native approach allows users to ask questions about page content, generate responses based on current context, or trigger prompts related to their workflow. Chrome extension architecture ensures compatibility with existing browsing habits.
Advantages include the friction-free invocation and context awareness. Users avoid tab switching or application launching delays when they need AI assistance. Integration with browsing activity means prompts can reference visible content automatically. Productivity gains accumulate through reduced context switching.
Limitations relate to the extension format. Advanced prompt engineering features like comprehensive testing frameworks, team collaboration, or extensive prompt libraries fall outside the core offering. The tool serves immediate assistance needs more than systematic prompt development.
Best suited for knowledge workers who spend significant time in browser-based workflows. Researchers reading articles, developers consulting documentation, writers gathering sources, and professionals conducting online research benefit from instant AI access. The keyboard shortcut appeals to users who value speed and minimal interface friction.
Camel AGI
Camel AGI explores multi-agent AI systems where different language model instances communicate and collaborate. The platform enables experimentation with autonomous agent interactions and task delegation patterns.
Key Points:
- Multi-agent AI system architecture.
- Communicative agents with distinct roles and objectives.
- Autonomous agent coordination and collaboration.
- Agent-to-agent dialogue capabilities.
- Experimental platform for advanced AI research.
- Task decomposition through specialized agents.
- Emergent problem-solving strategies exploration.
Fundamental approach involves configuring multiple AI agents with distinct roles and objectives, then observing how they coordinate to accomplish complex tasks. This communicative agent framework differs from single-prompt interfaces by introducing agent-to-agent dialogue and emergent problem-solving strategies.
Primary benefits center on exploring agentic AI architectures. Researchers studying autonomous systems, developers building multi-agent applications, and AI enthusiasts investigating frontier capabilities find value in the experimental platform. The approach reveals how task decomposition and specialized agents handle problems beyond single-model capabilities.
Challenges include the experimental nature and steeper learning curve. Multi-agent systems require understanding coordination patterns, agent design principles, and potential failure modes. Results can be unpredictable, making the platform more suitable for research than production deployment. Resource consumption increases with multiple concurrent model instances.
Target audience consists primarily of AI researchers, advanced developers, and technical enthusiasts exploring cutting-edge architectures. Academic research groups investigating agent collaboration, companies prototyping autonomous workflows, and individuals studying emergent AI behaviors represent typical users. The platform requires technical comfort and tolerance for experimental functionality.
Poe
Poe, developed by Quora, provides unified access to multiple language models through a single interface. The platform targets users who want to interact with different AI systems without managing separate accounts and subscriptions.
Key Points:
- Unified access to multiple language models including ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini.
- Seamless model switching within single interface.
- No-code bot creation capabilities.
- Rapid prototyping across different model architectures.
- Mobile and web platform availability.
- Consolidated billing and access management.
- Cross-platform experimentation support.
Core functionality includes seamless model switching between ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and other providers. No-code bot creation allows users to configure custom AI assistants without programming expertise. Rapid prototyping capabilities support experimentation across different model architectures. Mobile and web access ensures availability across devices.
Advantages center on accessibility and variety. Users can compare how different models handle identical prompts without switching platforms. The bot creation feature enables custom configurations for specific workflows. Consolidated billing and access management simplify the multi-model experience.
Considerations involve the abstraction layer. Users depend on Poe for model access rather than maintaining direct relationships with providers. Feature availability and model versions depend on integration agreements. Advanced capabilities specific to individual platforms may surface later in aggregated interfaces.
Best suited for users actively experimenting with multiple language models and seeking consolidated access. Developers building cross-platform applications, researchers conducting comparative studies, and businesses evaluating different AI providers benefit from the unified interface. The bot creation feature appeals to non-technical users wanting custom assistants without coding.
GPT Pilot
GPT Pilot positions itself as an AI-assisted development platform where developers maintain oversight while AI generates application code. The tool addresses the challenge of building complete applications through AI collaboration rather than isolated code generation.
Key Points:
- AI-assisted application development platform.
- Developer oversight with AI code generation.
- Incremental component and module creation.
- Iterative development with course correction.
- Human-in-the-loop validation.
- Accelerated development cycles.
- Reduced boilerplate code generation while preserving architectural control.
Platform mechanics involve describing application requirements, then working with AI to generate components, modules, and features incrementally. Developer oversight ensures code quality and architectural decisions align with project goals. The iterative approach allows course correction and refinement throughout development.
Primary strengths include accelerated development cycles and reduced boilerplate code generation. Developers focus on high-level design and validation while AI handles implementation details. The collaborative model preserves human decision-making authority while leveraging AI productivity gains.
Limitations involve the learning curve and trust calibration. Developers must understand when to accept AI suggestions versus intervening with manual corrections. Code review and testing remain essential since generated code requires validation. Complex architectural decisions still demand human expertise.
Target users include developers comfortable with AI-assisted workflows and willing to invest time learning collaborative development patterns. Solo developers building prototypes, small teams accelerating feature development, and programmers exploring AI tooling represent the core audience. Projects with clear requirements and standard architectures benefit most from the approach.
EmbedAI
EmbedAI enables businesses to create and embed custom AI chatbots into websites and applications. The platform focuses on making AI assistance accessible to customers and users through branded, domain-specific interfaces.
Key Points:
- Custom AI chatbot creation and embedding.
- Training on custom knowledge bases and documentation.
- Website and application integration.
- SaaS platform handling infrastructure and scaling. Customer-facing AI deployment.
- Branded chatbot interfaces.
- Domain-specific conversation design through prompt engineering.
Core capabilities revolve around chatbot creation, training on custom knowledge bases, and embedding in digital properties. Users configure chatbot behavior through prompt engineering, train models on company documentation and FAQs, then deploy to websites for customer interaction. The SaaS model handles infrastructure and scaling concerns.
Advantages include the end-to-end solution for customer-facing AI. Businesses avoid building chatbot infrastructure from scratch while maintaining control over knowledge sources and conversation design. Embedding options integrate chatbots into existing digital experiences without major platform changes.
Considerations center on customization limits within the platform constraints. Highly specialized chatbot requirements may exceed configuration options. Organizations with complex integration needs or unique conversation flows might require more flexible development platforms.
Best suited for businesses implementing customer support chatbots, lead qualification assistants, or information delivery systems. E-commerce sites, SaaS companies, educational institutions, and service providers benefit from automated customer interaction. Organizations seeking quick deployment without extensive development resources represent the target market.
Modelize.ai 1.0: AI Workflows
Modelize.ai provides auto-generated and expert-curated AI workflow templates. The platform addresses the challenge of translating business processes into effective AI prompt sequences.
Key Points:
- Auto-generated and expert-curated workflow templates. Multi-step AI process execution.
- Template customization for specific needs.
- Productivity-focused business workflows.
- Advertising and writing assistance templates.
- Web application with no installation required.
- Template library organized by use case and industry.
Functionality centers on workflow templates for common business tasks. Users select templates aligned with their needs, customize parameters, then execute multi-step AI processes. Template library organization surfaces productivity-focused workflows, advertising applications, and writing assistance patterns. Web application delivery eliminates installation requirements.
Primary benefits include reduced workflow design time and access to expert patterns. Users leverage proven sequences rather than developing prompts through trial and error. Template customization allows adaptation while maintaining underlying structure. The productivity emphasis addresses real business needs beyond experimental AI use.
Limitations relate to template availability and customization depth. Workflows outside available templates require manual development or adaptation. Complex business processes may not map cleanly to standardized templates. Users trade flexibility for convenience compared to building custom prompt sequences.
Target audience includes business professionals seeking productivity gains from AI without deep prompt engineering expertise. Marketing teams, operations managers, content strategists, and business analysts benefit from workflow templates aligned with professional tasks. Organizations standardizing AI usage across teams find value in curated template libraries.
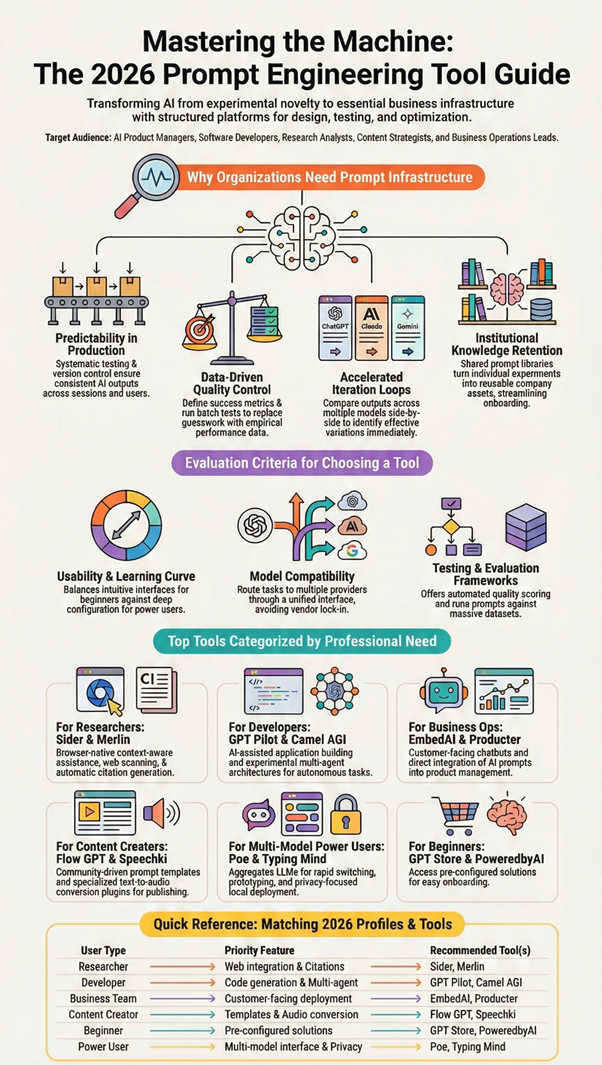
AI Prompt Engineering Tools Comparison by User Type
Different user types benefit from different tool characteristics based on their workflow requirements and technical sophistication. This comparison highlights how various AI prompt engineering tools serve distinct audiences.
Researchers and analysts working with web-based information sources gravitate toward browser-integrated tools like Sider and Merlin. These platforms minimize context switching and provide citation capabilities essential for academic and professional research. The ability to extract, annotate, and organize information without leaving the browser environment directly supports research workflows, making them top AI prompt engineering tools for knowledge workers.
Developers and technical teams require different capabilities. GPT Pilot serves developers building applications with AI assistance, while Camel AGI appeals to those experimenting with multi-agent architectures. Typing Mind attracts developers who value interface customization and self-hosted deployment options. Technical users generally prioritize integration options, API access, and control over hosting environment when selecting the best AI prompt engineering tools for their projects.
Content creators and marketing professionals benefit from tools emphasizing productivity and template libraries. Flow GPT and PoweredbyAI provide prompt collections for common creative tasks, often available as free AI prompt engineering tools. Modelize.ai offers workflow templates for marketing and writing applications. Speechki serves creators working across text and audio formats. These users value ready-made solutions over building custom frameworks.
Business teams implementing customer-facing AI need different functionality. EmbedAI supports chatbot deployment for customer service. Producter integrates AI capabilities into product management workflows. Poe enables multi-model experimentation for organizations evaluating different providers. Business users prioritize deployment ease, customer experience, and integration with existing business systems when choosing the best AI prompt engineering tools app for enterprise use.
Individual users exploring AI capabilities or seeking prompt inspiration find value in discovery platforms. The GPT Store provides access to pre-configured assistants for specific tasks. PoweredbyAI and Flow GPT offer community-contributed prompts across diverse categories. These platforms lower the entry barrier for non-technical users while providing variety, making them accessible top AI prompt engineering tools for beginners.
AI Prompt Engineering Tools Comparison
| Tool Name | Primary Use Case | Best For | Key Strengths | Limitations | Ideal User Type |
| Sider: AI Research Agent & Extension | AI-powered research and prompt-assisted browsing | Researchers, analysts, content strategists | Browser-native research, citations, multi-model support, visual reports | Advanced features may feel complex for beginners | Researchers, knowledge workers |
| Typing Mind | Prompt creation and daily AI interactions | Power users, prompt engineers | Clean multi-model UI, local/self-hosted setup, prompt libraries | Limited built-in research features | Advanced users, privacy-focused teams |
| GPT Store | Discover and use custom GPTs | General users, productivity-focused teams | Access to specialized GPTs, marketplace-style discovery | Limited customization of underlying prompts | Non-technical users |
| Speechki ChatGPT Plugin | Convert AI text outputs into audio | Content creators, accessibility users | Text-to-speech inside ChatGPT, multilingual support | Focused only on audio output, not prompt design | Creators, educators |
| PoweredbyAI | Prompt discovery and AI tools hub | Beginners exploring AI tools | Ready-made prompts, free access, broad tool coverage | Less control over prompt experimentation | Beginners, solo creators |
| Flow GPT | Prompt sharing and prompt libraries | Prompt explorers, productivity users | Community-driven prompt discovery, categorized libraries | Limited prompt testing or evaluation tools | Prompt learners, creators |
| Producter | Product management with AI workflows | SaaS founders, product managers | Customer-centric tools, changelog automation, workflow support | Not dedicated solely to prompt engineering | Product teams |
| Merlin Chrome Extension | Browser-based AI prompt execution | Daily productivity users | Quick access via browser, multi-use AI commands | Limited depth for complex prompt testing | Professionals, marketers |
| Camel AGI | Multi-agent prompt experimentation | AI researchers, agent developers | Communicative agent frameworks, experimental workflows | Steep learning curve | AI researchers |
| Poe | Multi-model chat and bot creation | Builders, tinkerers | Access to multiple LLMs, no-code bots, fast prototyping | Limited prompt versioning tools | Developers, AI hobbyists |
| GPT Pilot | AI-assisted app development | Software developers | End-to-end app generation, prompt-driven coding | Requires technical knowledge | Developers |
| EmbedAI | Embedded AI experiences | SaaS builders, startups | Create and deploy embedded AI tools | Limited advanced prompt analytics | SaaS teams |
| Modelize.ai | Prompt-based AI workflows and templates | Marketers, productivity teams | Prebuilt workflows, templates, automation | Less flexibility for deep customization | Business users |
Frequently Asked Questions
How do prompt engineering tools integrate with browsers, IDEs, or extensions?
Integration approaches vary by tool design and target workflow. Browser extensions like Sider and Merlin operate as sidebars or keyboard-activated overlays that interact with webpage content. These extensions access visible text, provide contextual assistance, and generate citations without requiring users to switch applications. The browser-native approach works well for research, content analysis, and web-based workflows.
IDE integrations and developer-focused platforms typically offer API access, command-line interfaces, or code editor plugins. GPT Pilot exemplifies the development environment integration approach, allowing developers to maintain their preferred tools while incorporating AI assistance. Multi-model platforms often provide unified APIs that abstract provider differences, simplifying integration across different systems.
Are prompt engineering tools useful for non-developers?
Absolutely. Many platforms specifically target non-technical users through intuitive interfaces and pre-built templates. The GPT Store eliminates prompt engineering entirely by providing ready-made assistants. Flow GPT and PoweredbyAI offer prompt libraries organized by common tasks, allowing users to adopt proven patterns without understanding underlying engineering principles. These represent some of the best AI prompt engineering tools for users without coding experience.
Business professionals, content creators, researchers, and students benefit from tools that streamline prompt reuse and organization. Typing Mind improves daily AI interaction for knowledge workers regardless of technical background. EmbedAI enables businesses to deploy chatbots without development expertise. The key distinction in this AI prompt engineering tools comparison lies between platforms requiring prompt engineering knowledge versus those providing curated experiences built by experts. Many free AI prompt engineering tools offer sufficient functionality for casual users to achieve professional results.
Do these tools work with multiple AI models?
Multi-model support varies significantly across platforms. Poe explicitly provides unified access to ChatGPT, Claude, Gemini, and other models through a single interface. Sider routes different tasks to appropriate models including ChatGPT, Claude, DeepSeek, and Gemini based on requirements. Typing Mind enables seamless switching between providers while maintaining conversation history.
Single-provider tools like the GPT Store and some ChatGPT plugins work exclusively within their ecosystem. Platform-specific solutions offer deeper integration with particular models but limit flexibility. Organizations evaluating multiple providers benefit from tools that abstract model differences and enable comparative testing. The trend favors platforms supporting multiple models as users recognize different models excel at different tasks.
How do prompt libraries improve productivity?
Prompt libraries eliminate repeated work by storing tested prompts for reuse. Rather than recreating effective prompts from memory or notes, users access organized collections categorized by use case. This accumulated knowledge becomes an organizational asset that new team members can leverage immediately.
Quality control improves when teams share and refine prompts collectively. Popular prompts receive usage feedback and iterative improvements from multiple contributors. Organizations can establish prompt standards that ensure consistent AI output quality across different users and departments. The library approach transforms ad hoc experimentation into systematic knowledge management.
What should beginners prioritize when choosing tools?
Beginners benefit from platforms minimizing setup complexity and providing curated experiences. The GPT Store offers the lowest entry barrier through pre-configured assistants requiring zero prompt engineering. Flow GPT provides community-tested prompts with clear descriptions and use cases. PoweredbyAI combines tool discovery with prompt examples, helping newcomers understand practical applications.
Interface simplicity matters more than advanced features for new users. Typing Mind delivers straightforward chat improvements without overwhelming configuration options. Browser extensions like Merlin integrate naturally into existing workflows rather than requiring new habits. Starting with focused, user-friendly tools builds confidence before graduating to more sophisticated platforms offering greater control and customization.
What is the difference between free AI prompt engineering tools and paid versions?
Free AI prompt engineering tools typically offer core functionality like basic prompt storage, simple testing, and access to community libraries. Platforms like Flow GPT, PoweredbyAI, and the GPT Store provide substantial value without subscription costs. These options work well for individuals, students, and small teams exploring AI capabilities or handling modest prompt management needs.
Paid versions and premium AI prompt engineering tools generally add advanced features including team collaboration, version control, sophisticated testing frameworks, priority API access, and enhanced storage limits. The best AI prompt engineering tools for enterprise use offer security features, compliance certifications, dedicated support, and integration options beyond what free tiers provide. Organizations requiring reliable performance, accountability, and scalability often find premium subscriptions justify the investment through improved productivity and reduced risk.
Final Takeaway
AI prompt engineering tools have evolved from experimental utilities into essential infrastructure for reliable AI deployment. Organizations moving beyond casual AI experimentation toward production workflows require the consistency, testing capabilities, and collaboration features these platforms provide. Whether exploring free AI prompt engineering tools or investing in premium solutions, the right choice depends on specific workflow requirements.
The diversity of available options in this AI prompt engineering tools comparison reflects genuine differences in use cases and user requirements. Researchers need citation and knowledge management capabilities that developers building autonomous agents do not prioritize. Content creators benefit from template libraries that technical teams might bypass in favor of granular control. Business teams implementing customer-facing chatbots require deployment and integration features distinct from individual productivity tools. The best AI prompt engineering tools app for one user may prove inefficient for another.
Long-term value emerges from matching tool capabilities to actual workflow needs rather than chasing comprehensive feature sets. Specialized platforms serving specific use cases often deliver better results than general-purpose alternatives attempting universal coverage. As AI capabilities continue advancing, the top AI prompt engineering tools enabling effective prompt design, testing, and management will remain relevant regardless of which specific models dominate future markets.
Success with AI prompt engineering tools ultimately depends on systematic approach rather than tool selection alone. Organizations that invest in building prompt libraries, establishing evaluation criteria, and sharing knowledge across teams extract more value than those expecting tools to solve workflow challenges automatically. The platforms covered here provide the infrastructure, but effective usage requires commitment to deliberate practice and continuous refinement.